VICTORY
FACTS
FACTS
Everything for the front, everything for victory
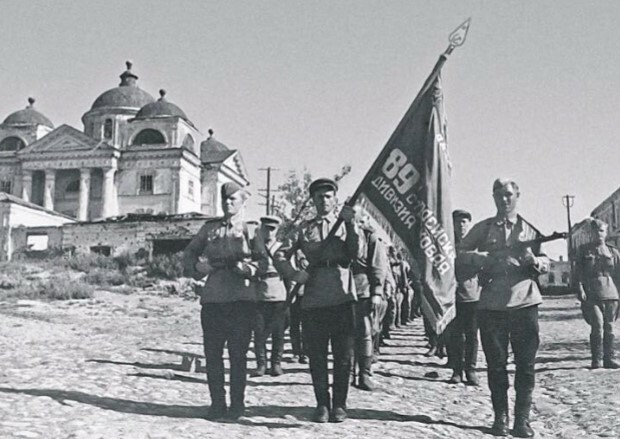

During the years of the Great Patriotic War, more than 600,000 residents of the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic were drafted into the army. In the military mobilization work carried out in the republic at the initial stage of the war, a special place was occupied by the formation of national and international divisions...
The Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic, together with the entire Soviet Union, rose to defend the fatherland from Nazi Germany.
From the very first days of the war, the party and state bodies of Soviet Armenia, the executive committees of local councils, city and district military commissariats joined in the work of restructuring military and economic resources for the needs of the front...
From the very first days of the war, the party and state bodies of Soviet Armenia, the executive committees of local councils, city and district military commissariats joined in the work of restructuring military and economic resources for the needs of the front...
Armenian Soviet Socialist
Republic - Contribution to Victory
Republic - Contribution to Victory
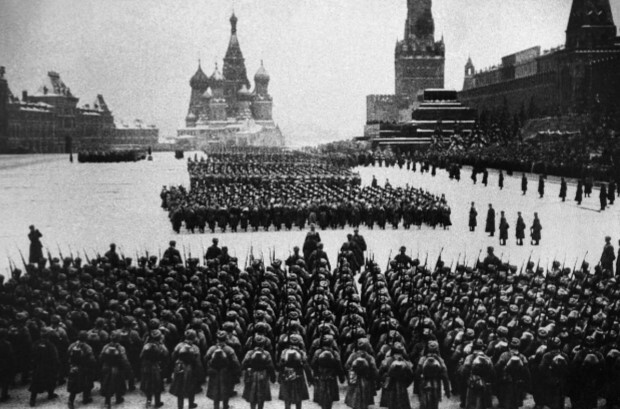
Military parade on November 7


Despite the fact that the situation in Bessarabia was generally in favor of the USSR and the Moldavian border was not crossed by the Romanians, and on this sector of the front the USSR had more forces than Romania, on June 29 the Soviet armies began to prepare for a retreat from the Moldavian SSR.
Retreat of Soviet troops from the Moldavian SSR
On June 22, the Third Reich attacked the USSR, and battles began on the western borders of the Soviet Union. The defensive operation began in Moldova. At the same time, the Romanian leadership, without concluding any agreements on joint military operations with Germany, ordered its troops to cross the Prut River...
Defensive operation in Moldova


In the first months of the war, the mobilization of conscripts began on the territory of the Moldavian SSR. The Chisinau Communist Fighter Regiment (commander - P.A. Orlov, commissar - Ya. A. Mukhin), over 60 urban and rural fighter battalions were created.
Mobilization of those liable for military service on the territory of the Moldavian SSR
The Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic entered the Second World War along with the entire Soviet Union.
The main blow fell on it from Romania, which, with the support of the Third Reich, occupied Bessarabia and the area between the Southern Bug and Dniester rivers. The territories occupied by the Romanians became part of Great Romania, and returned under the control...
The main blow fell on it from Romania, which, with the support of the Third Reich, occupied Bessarabia and the area between the Southern Bug and Dniester rivers. The territories occupied by the Romanians became part of Great Romania, and returned under the control...
Occupation of the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic




In Serbia, subordinate to the German government, by the fall, the activities of partisans and Chetniks against the occupation forces intensified. On October 10, the authorized general command in Serbia, Franz Boehme, gave the order to shoot for each killed German soldier 100 civilians, for each wounded - 50.
Partisan movements in Serbia
Genocide of Serbs (1941-1945) - the destruction, persecution and discrimination of Serbs during the Second World War on the territory of the occupied Kingdom of Yugoslavia. The exact number of victims is still unknown. According to various estimates, it was as a result of the genocide that from 197,000 to 800,000 people died. The main organizers of the genocide were the fascist Ustasha regime in the Independent State of Croatia and the German occupation administrations.
Genocide in Serbia
On March 25, 1941, under pressure from Germany, Yugoslavia joined the Triple Pact (Germany, Italy and Japan). But on March 27, a military coup took place in the country: the army, with the support of the population, removed the regent and proclaimed Peter II the autocratic king. On April 6, 1941, German troops invaded Yugoslavia and occupied the country for two weeks. In August 1941, the Germans created a puppet "Serbian government" in Belgrade.
Partisan movements in Serbia
Herring for Churchill
The rapid advance of German troops to the east in the summer and autumn of 1941 led to the loss of fisheries in Transnistria, Crimea, on the coast of the Baltic and the Black Sea Caucasus.
The population of the Soviet Union was not pampered with fish delicacies even in peacetime. But the British, under the conditions of the underwater blockade of the island, suffered without their usual fish cuisine.
The population of the Soviet Union was not pampered with fish delicacies even in peacetime. But the British, under the conditions of the underwater blockade of the island, suffered without their usual fish cuisine.
Life of Ugra residents during the Second World War
On January 1, 1942, 91,226 people lived in the district. The population was replenished due to a new wave of special contingents and evacuated citizens. This created additional pressure on the available food resources. In the navigation of 1942, the Germans (1754 people from the Leningrad region) and more than a thousand children were taken out from the besieged Leningrad. The children suffered from dystrophy, were so weak that many could not walk on their own.
Berezovsky glass plant
On July 31, 1942, the executive committee of the Omsk Regional Council of Working People's Deputies made a decision to build a glass factory in the Berezovsky region at a quartz sand deposit.
The site for the construction of a glass factory is directly adjacent to the sand deposit. A reconnaissance survey of the right bank of the Vogulka River at its confluence with Sosva identified reserves of quartz sands by a geological exploration expedition in the amount of more than 1 million tons.
The site for the construction of a glass factory is directly adjacent to the sand deposit. A reconnaissance survey of the right bank of the Vogulka River at its confluence with Sosva identified reserves of quartz sands by a geological exploration expedition in the amount of more than 1 million tons.
Fraternal assistance to Ukraine
At the initiative of the party and Komsomol bodies of organizations, the workers of the Omsk region took patronage over the Zaporozhye region of Ukraine liberated from the Nazis.
The Omsk Regional Committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks did a lot of work at industrial enterprises in the collective and state farms of the region.
The Omsk Regional Committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks did a lot of work at industrial enterprises in the collective and state farms of the region.
Cedar woman
Khanty composed legends about their compatriot Anna Efimovna Moldanova (1895-1972). "Woman-Cedar" - so respectfully called her for her beauty, strength and firmness of spirit. Anna was born into the family of a Khanty nomad-reindeer breeder in the Yuil yurt association of the Berezovsky district of the Kazym foreign council. From her youth, Anna, as the eldest daughter, began to engage in hunting and fishing, hunting not only fur-bearing animals, but also bears, wolves, elks.
Hospitals patronage
The general care of the residents of the district was surrounded by military personnel who were being treated in hospitals in Tyumen. In the Khanty-Mansiysk district, the patronage work was headed by the district commission under the leadership of the first secretary of the district committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks V.V. Uzentsev. In 1942, when hospitals for seriously wounded soldiers and commanders opened in Tyumen, the staff of the largest enterprise in the city, the Samarovskiy Fish Cannery, took over their patronage.
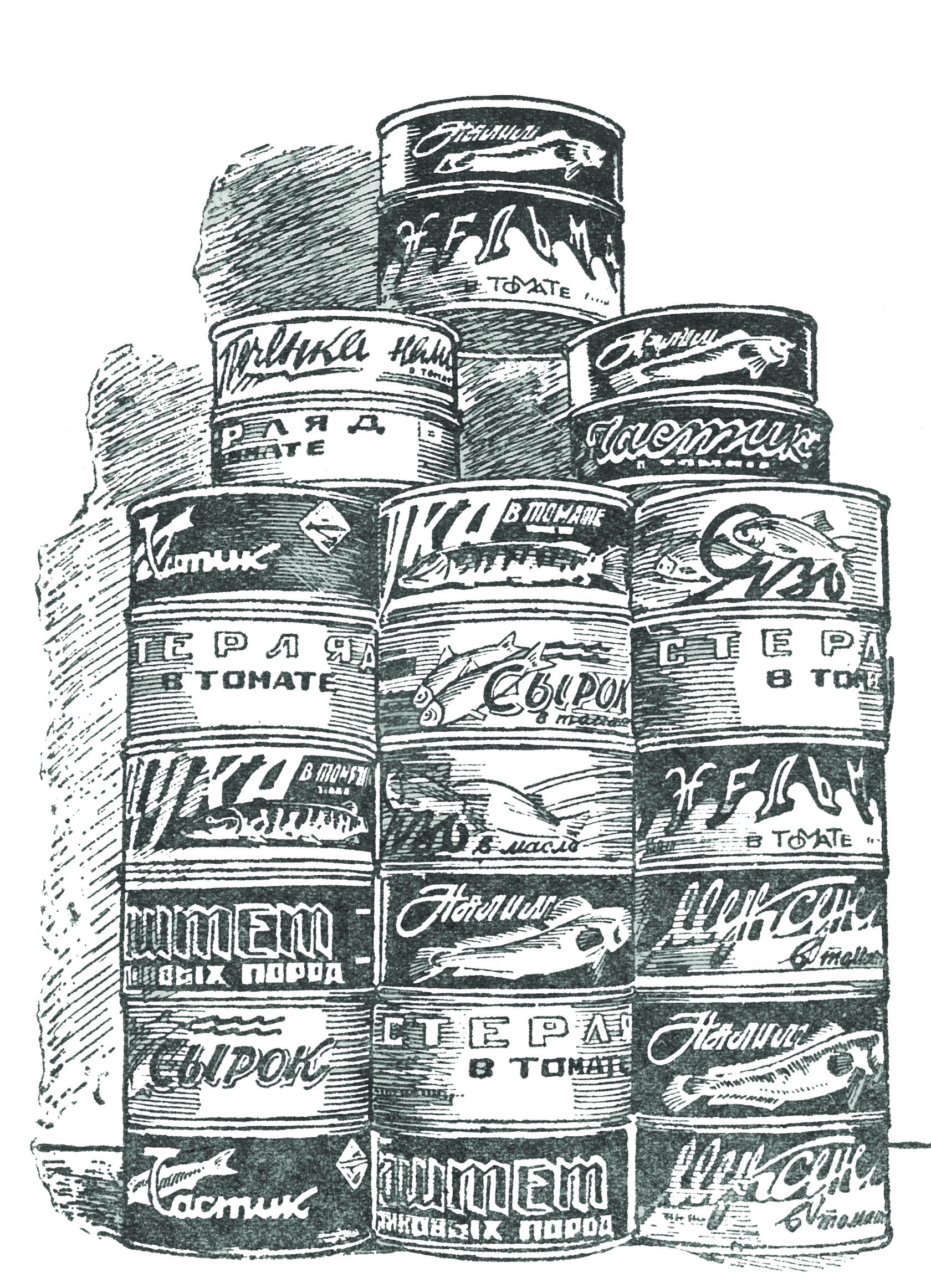

Canned foods for the front
During the war, the Samara fish cannery produced millions of cans of fish delicacies: ide, pike and sturgeon. What the soldiers especially liked was carp with buckwheat porridge. The fish was cleaned manually. Salted fish was produced in large quantities as well. It was sent to the front in wooden barrels. More than three hundred fish cannery workers went off to war.

On the activities of the KhMNO strongpoints during the war
The situation that developed during the war put the Soviet economy in very difficult conditions. The work of scientific centers located in the regions of the Urals and Kazakhstan, including Siberia, was strengthened.

War on illiteracy
Surprisingly, in 1942, when there were heavy battles at the front, the German fascist troops were advancing into the interior of the country, another war was declared in the district - against illiteracy.


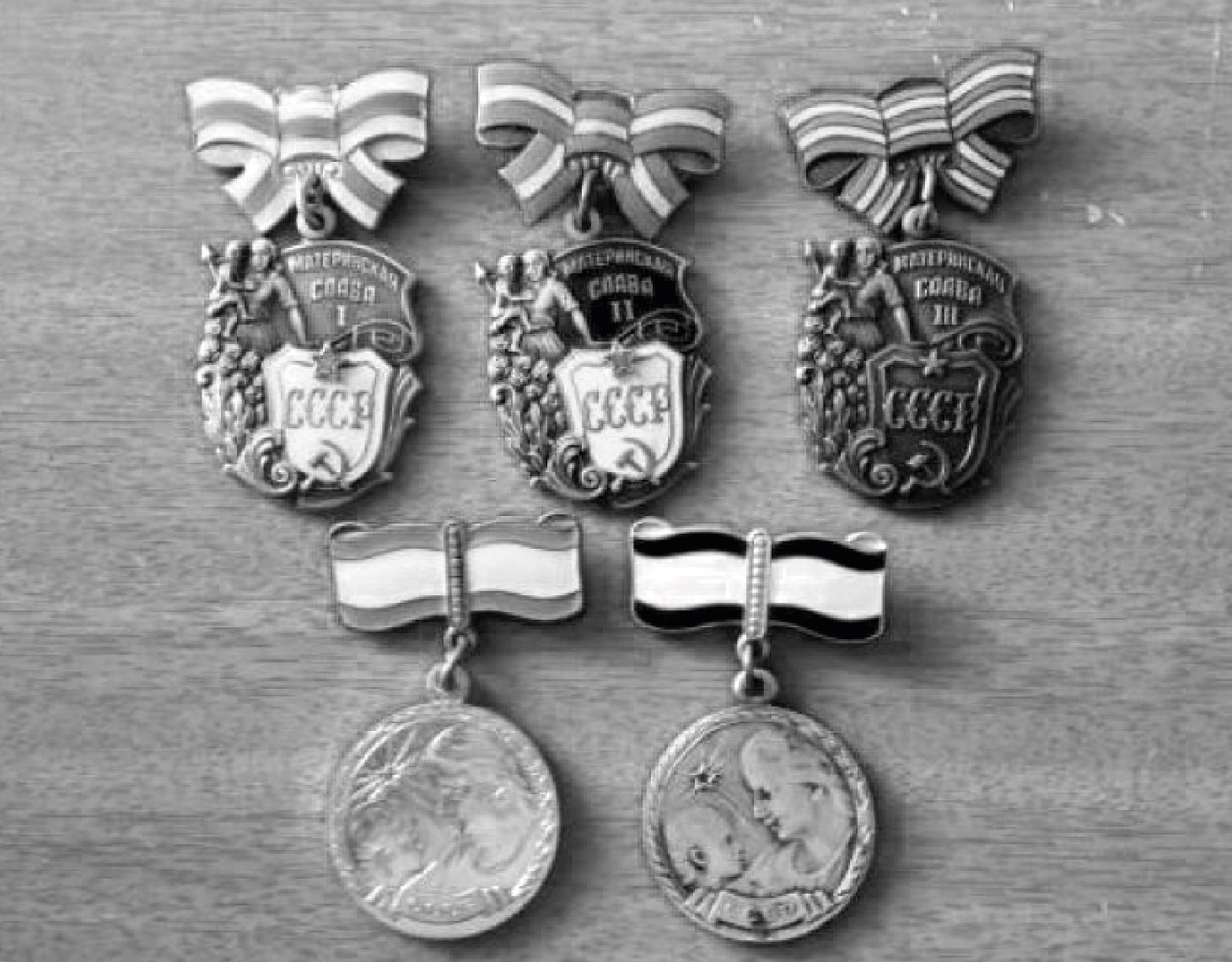
Mother Heroine
On July 8, 1944, a decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR was issued "On increasing state aid to pregnant women, mothers with many children and single mothers, strengthening the protection of motherhood and childhood, establishing the honorary title" Mother Heroine ", establishing the Order" Maternal Glory "and the Medal of Motherhood ".


Skiing is not fun, it's a weapon
During the war years, the district's newspapers urge young people to get up on skis. In 1944, a traditional Komsomol-trade union cross named after the 26th anniversary of the Red Army was held in the district.


Victory Day
And here it is, the long-awaited issue of the newspaper "Stalin's Tribuna" on May 10, 1945. On the front page, next to the portrait of Stalin, there is a decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR "On declaring May 9 the Victory Day". And after the decree - the Act on the unconditional military surrender of the German armed forces.
The second page of the newspaper tells how the news of the surrender of Hitlerite Germany was greeted in Khanty-Mansiysk.
The second page of the newspaper tells how the news of the surrender of Hitlerite Germany was greeted in Khanty-Mansiysk.
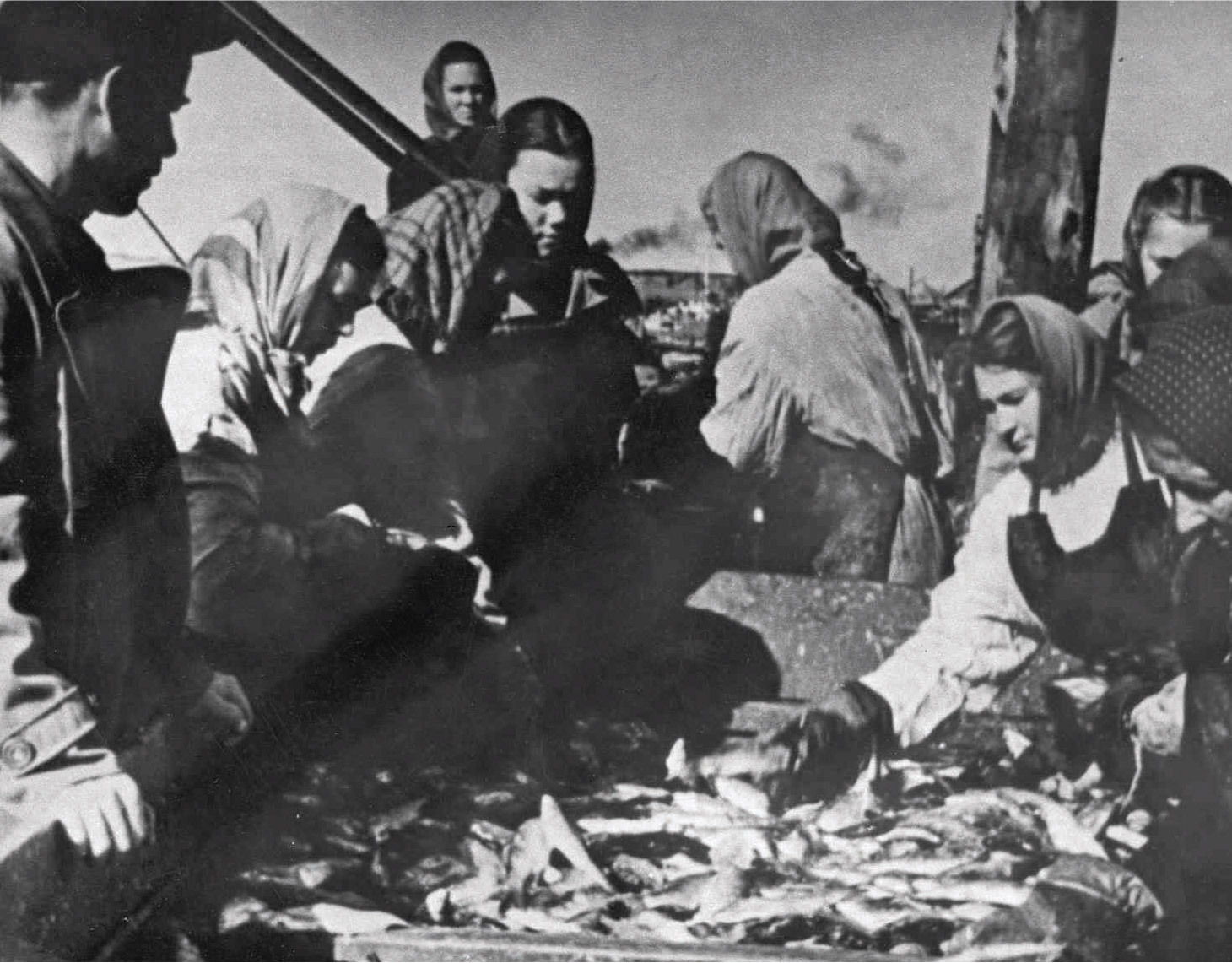
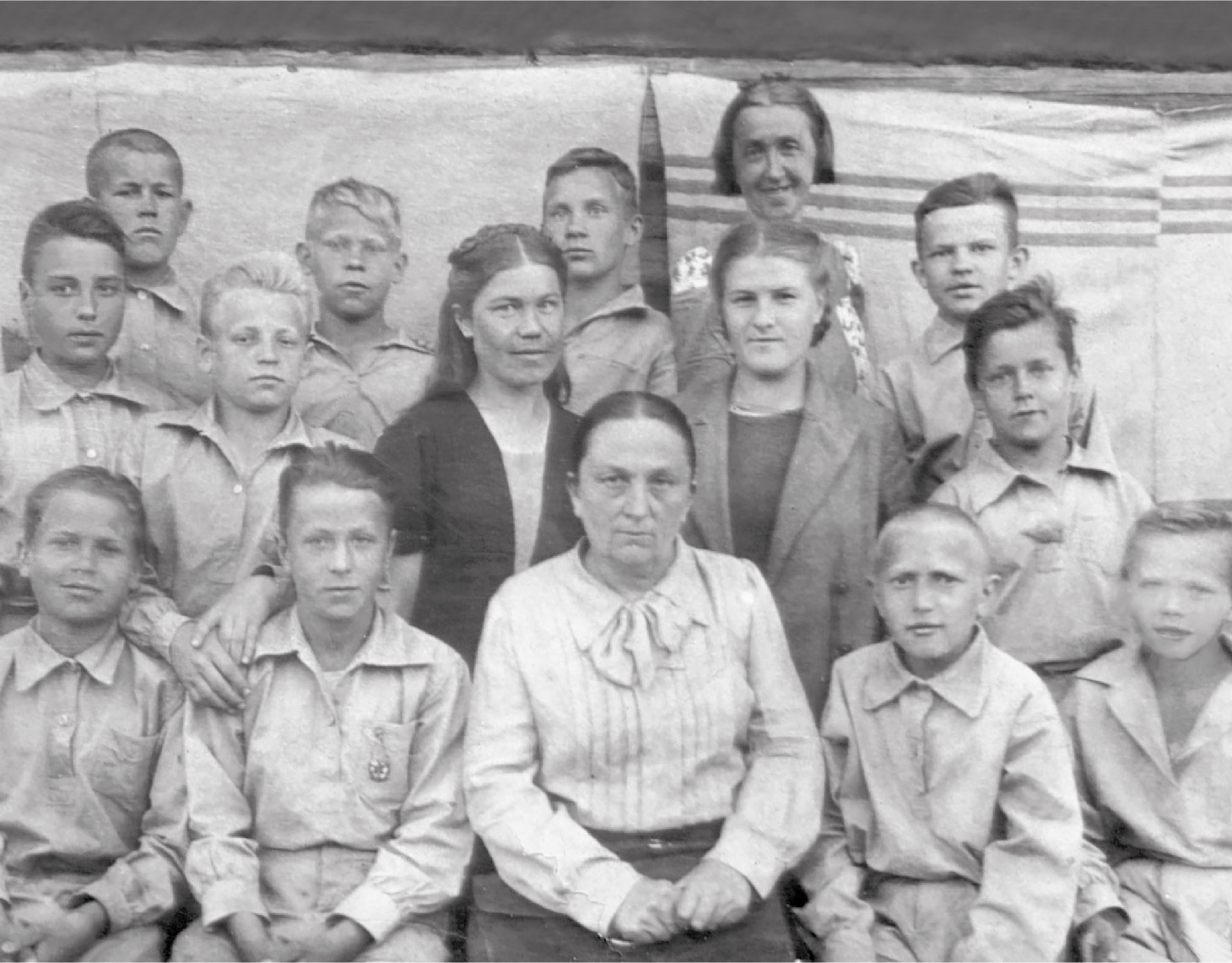
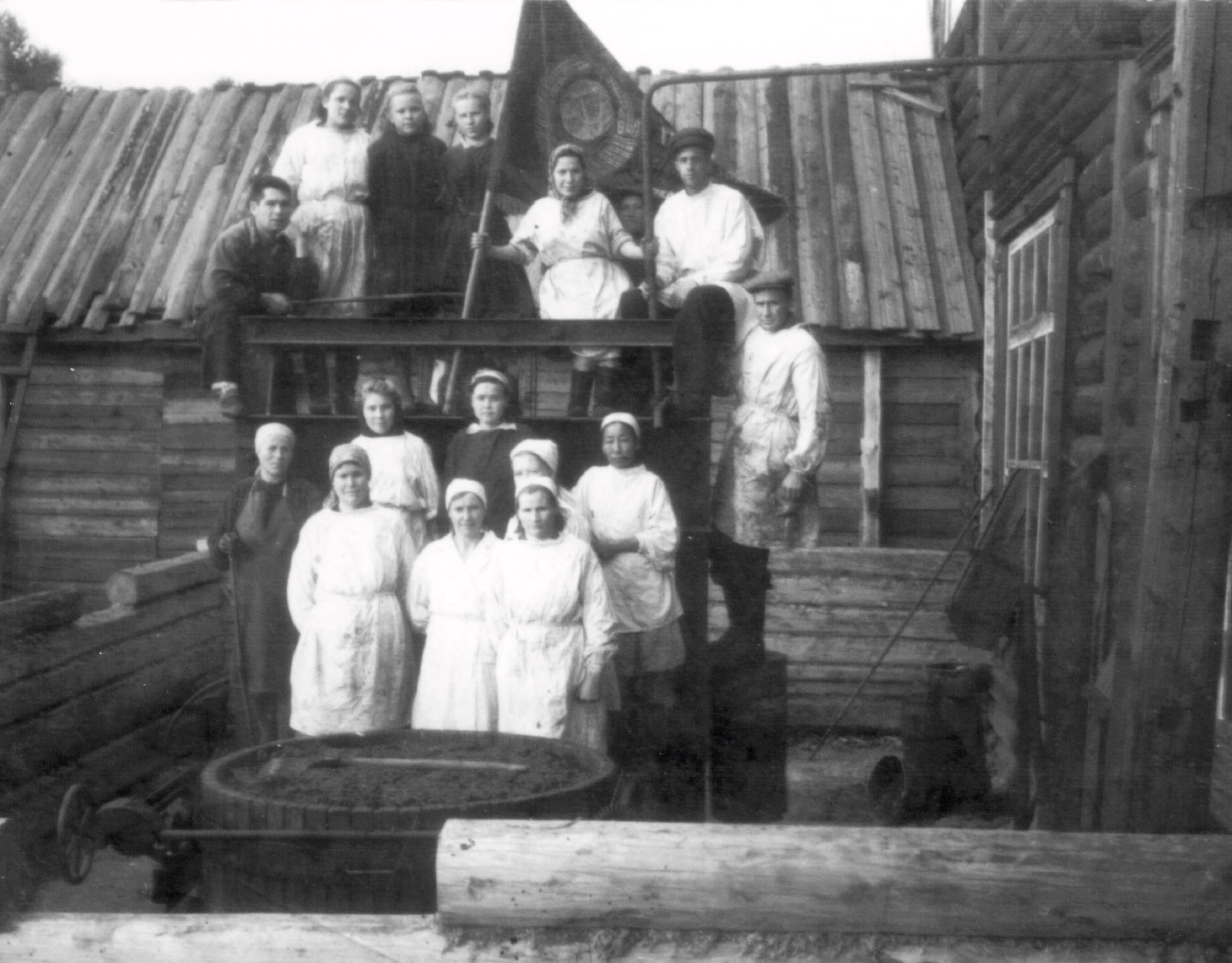
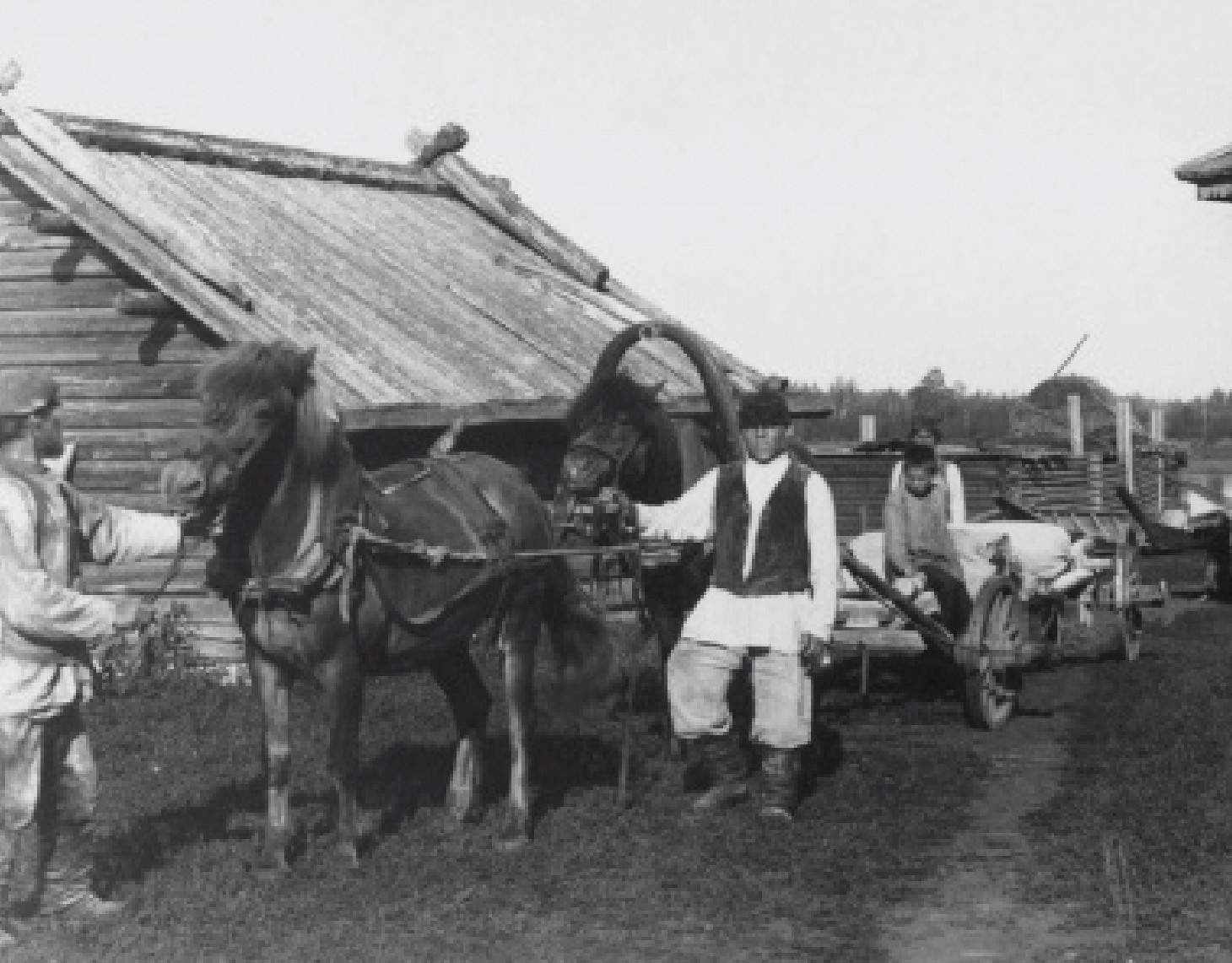







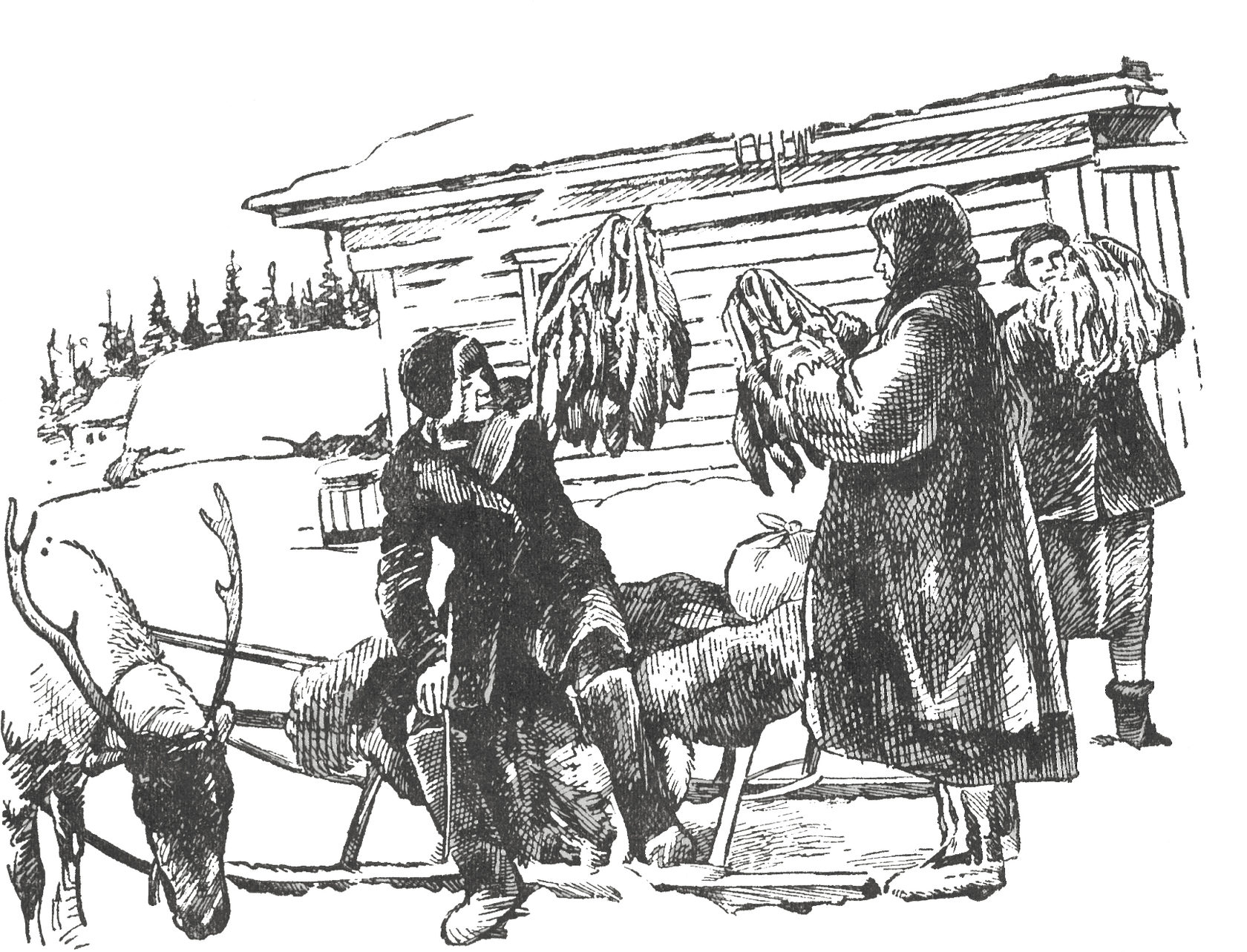
"Soft gold of Ugra"
During the war, the fur production became of defensive importance, since it was used to pay for lend-lease supplies. Since the departure of many male hunters to the front by the year 1943, the production of furs decreased a little. But already in 1944, the women, old men and young people who replaced them provided the state with furs at a cost of 5.9 million rubles.
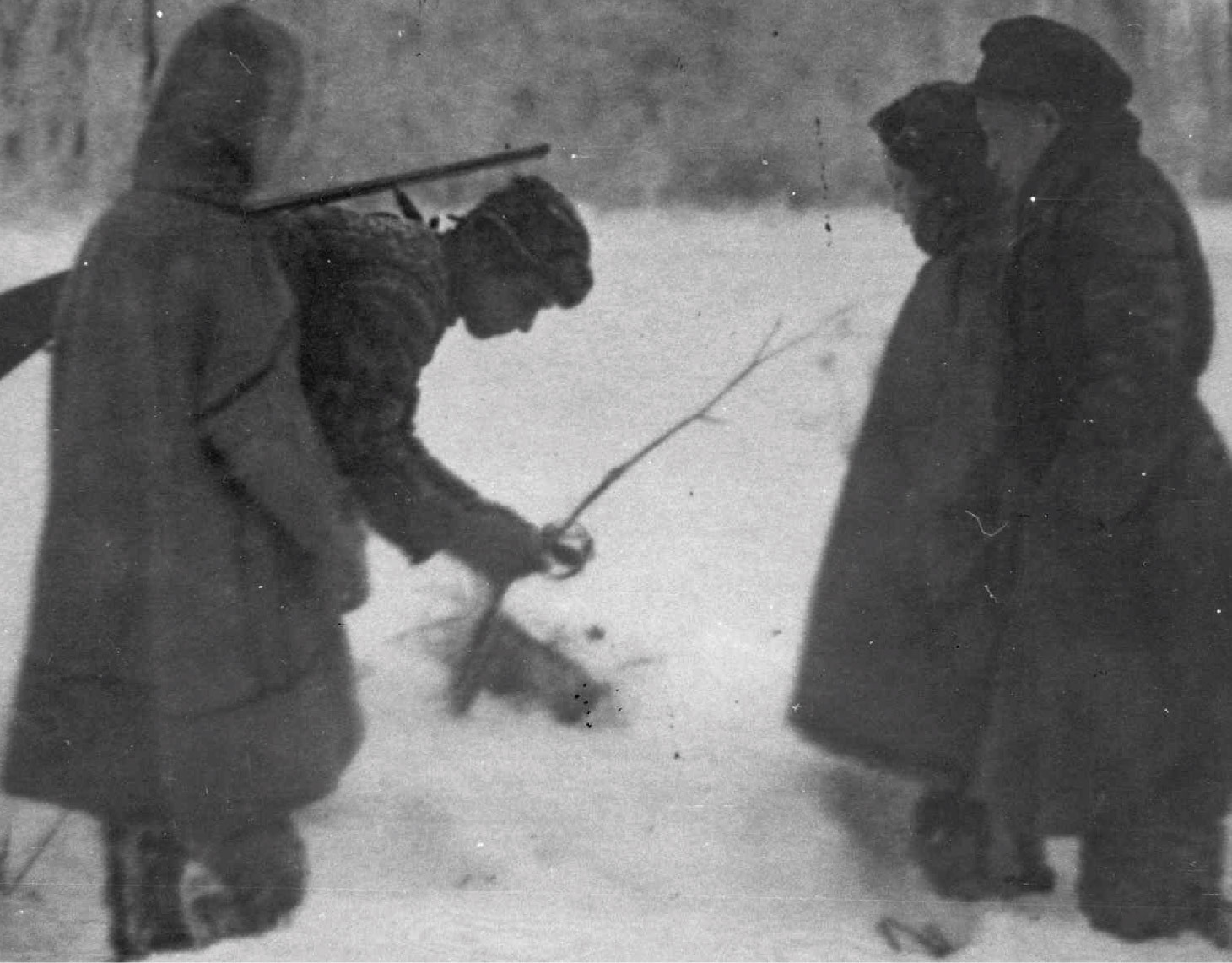


Propaganda brigade
During the war in KhMNO, a special role belonged to the workers of the "ideological front". They supported the morale of the population, encouraged patriotic actions, strengthened faith in victory, called for selfless work and assistance to the front.
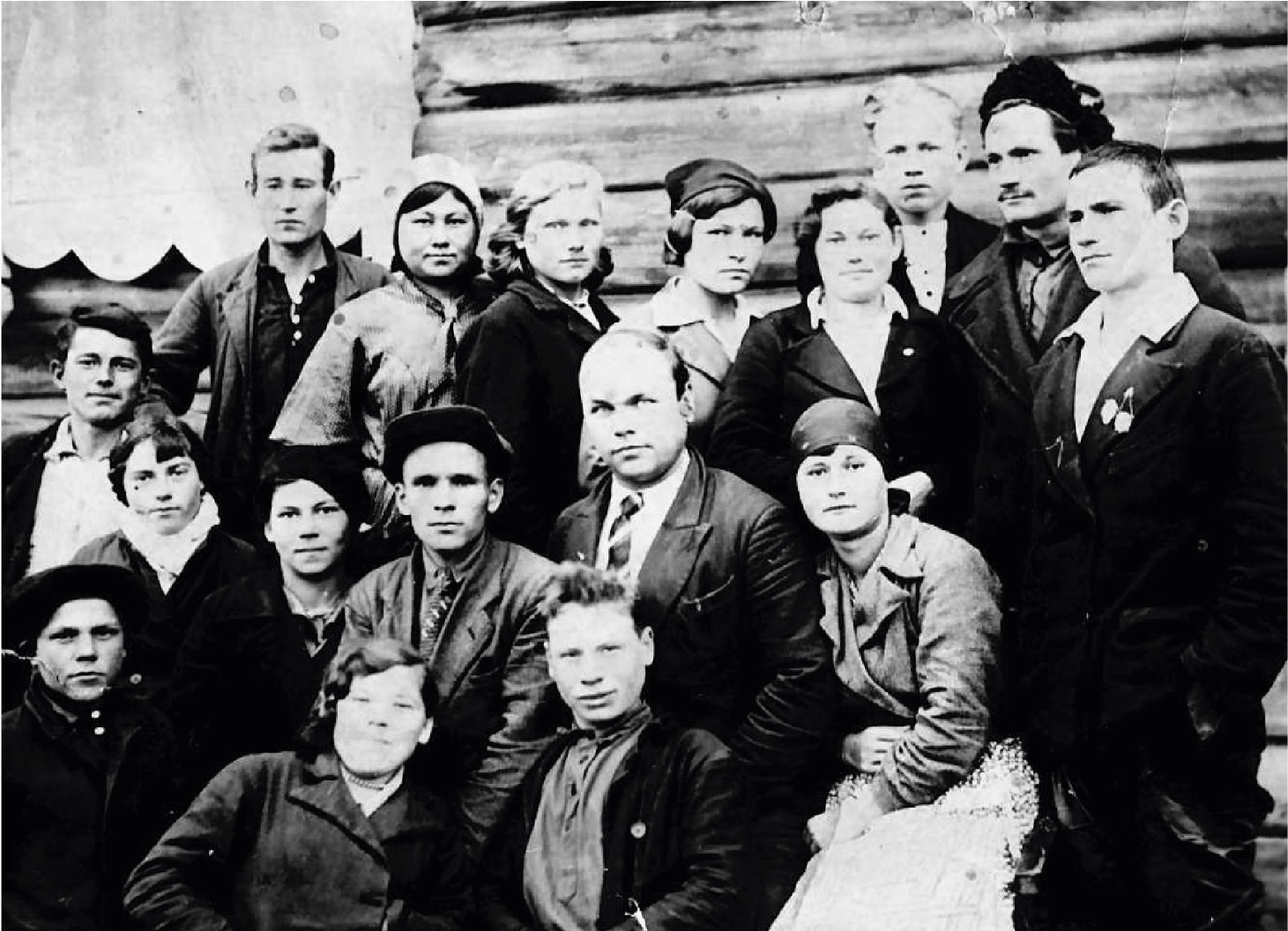

Cultural front
The war made its own adjustments to the activities of cultural institutions. The main content of the work was an explanation of the nature and purpose of the war, coverage of its course, exposure of the essence of fascism, propaganda of the heroic deeds of Soviet people in the rear and at the front.
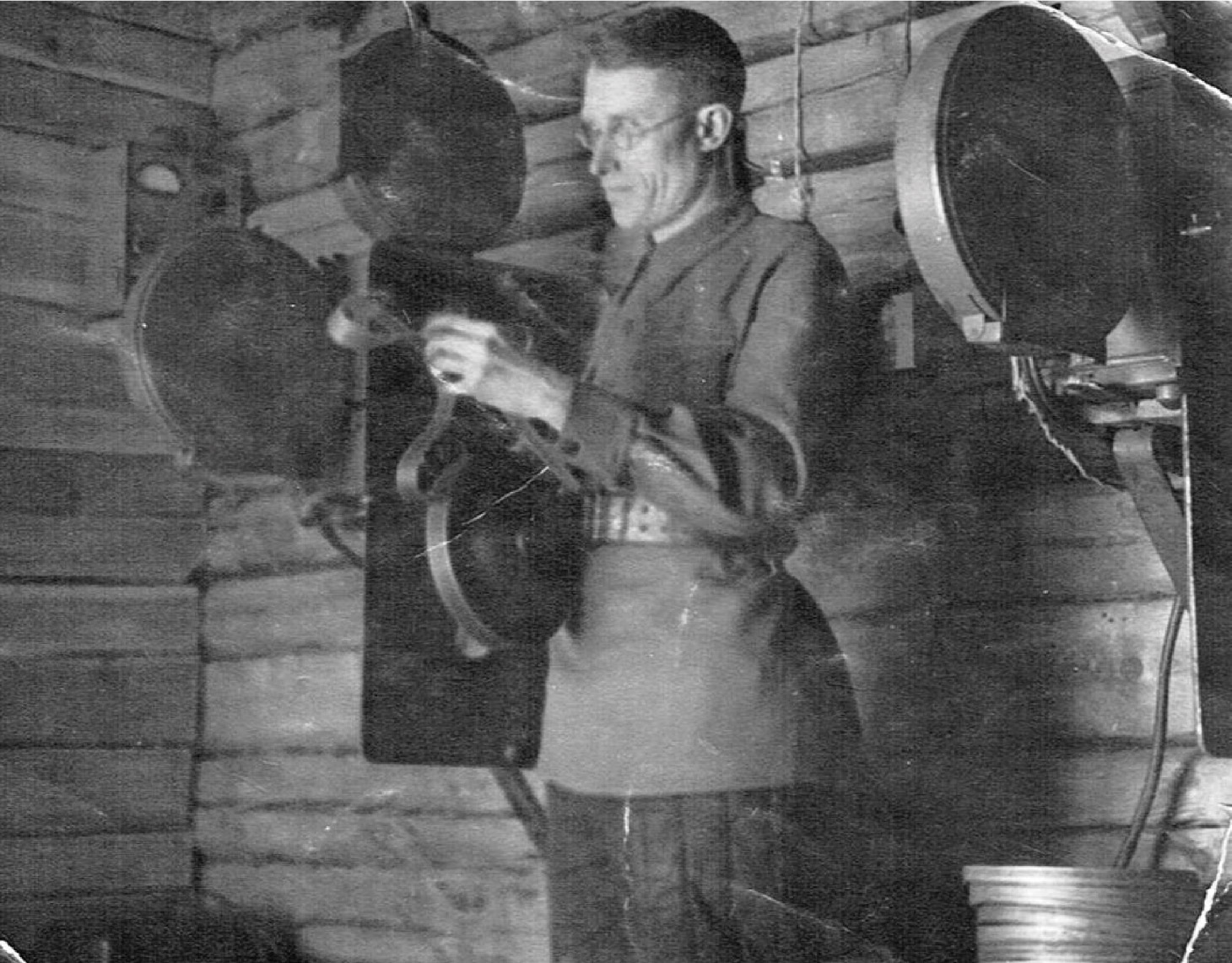


Wild plants for the front
During the war, the Nakhrachinsky plant launched a dry-vegetable shop with an annual capacity of 400 tons. Back then, the plant employed 137 people. During April 1942 alone, the plant produced: cranberry extract – 1,819 kg, rowan extract – 1,524 kg, blueberry extract – 431 kg, cranberry extract –993 kg; jam – 501 kg, berry wine – 1,701 liters, dry enzyme – 171 kg. The locals, especially schoolchildren, brought berries and crude drugs to the plant for processing every season.
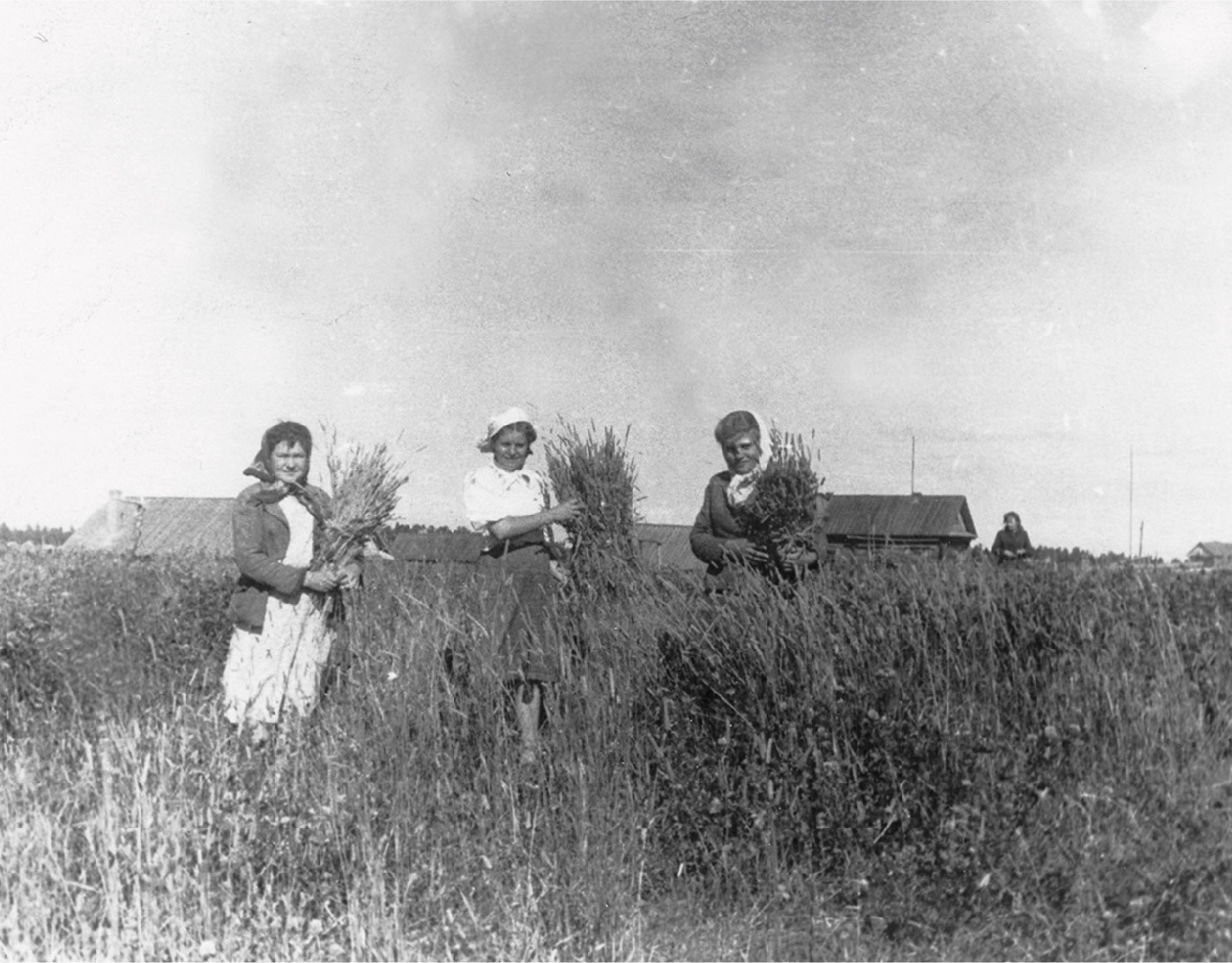


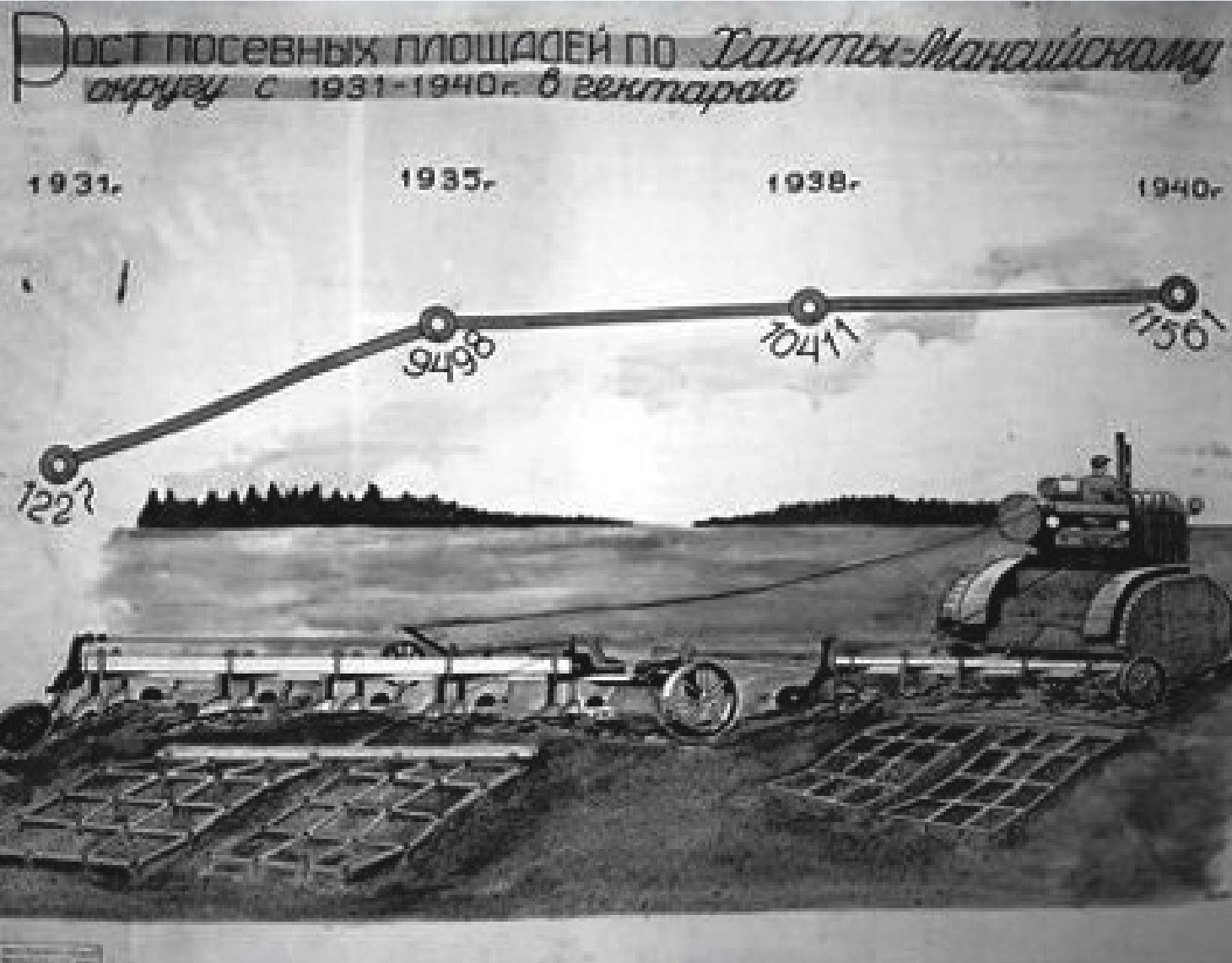
Ugra agriculture and forestry during the war
The development of agriculture in Khanty-Mansiysk National Okrug was a forced measure, it has become a necessity in order to provide the population of the okrug with food. In total, there were 298 collective farms in the district, 70 of them were agricultural artels.
Extracts for the victory
On October 1, 1938, in the village of Nakhrachi, Kondinsky district (now an urban-type settlement Kondinskoye) the Nakhrachi extract producing factory has been fully put into operation. Berries came from all over the okrug the factory produced hundreds of tons of extract, wines, jams, medicinal raw materials. In addition, the factory was engaged in the production of food, developed a subsidiary farming, prepared wood, because even electricity at that time was generated by a steam engine that worked on firewood.
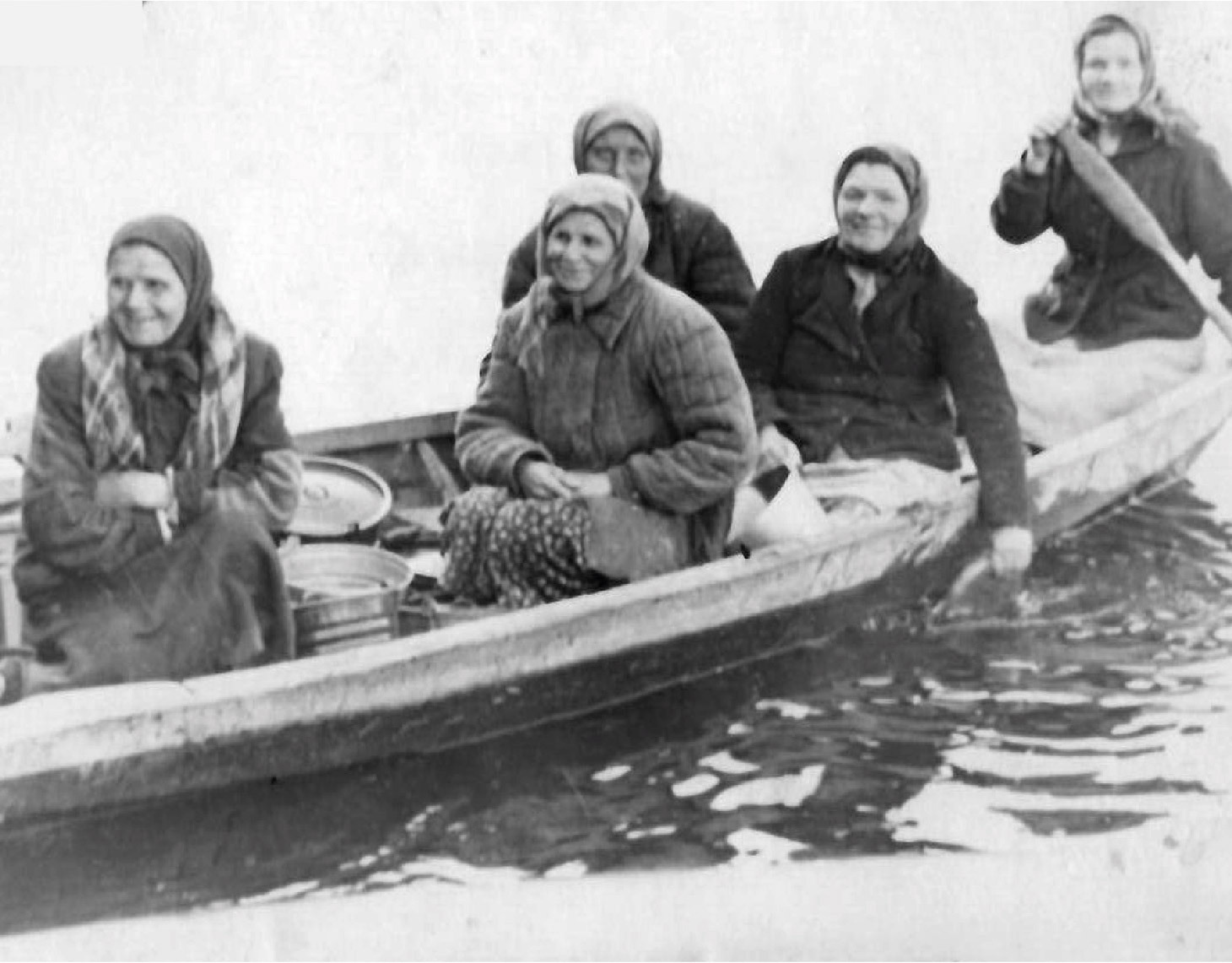
"Fish Front"
In spring 1942, another front, Ob — Irtysh, was added to the10 fronts of the Great Patriotic War. How did the "Fish Front" occur in the north of the Western Siberia? The losses of the main fishing territories in the European part of the USSR put the task of filling the shortage of fish at the expense of the eastern regions of the country on the agenda. The decree of the USSR Council of People's Commissars - Sovnarkom and Central Committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks of January 6, 1942, was crucial for the development of the fishing industry in Ugra.
Leningrad orphanages in Ugra
On July 28, 1942, at a meeting of the executive committee of the Council of Workers' Deputies of the Khanty-Mansiysk National Okrug, a decision on lodging of evacuated children arriving to the okrug from Leningrad was made.
In autumn, 1942, 10 Leningrad orphanages with 782 school-age children and 162 preschool-age children were evacuated to the Khanty-Mansiysk National Okrug.
In autumn, 1942, 10 Leningrad orphanages with 782 school-age children and 162 preschool-age children were evacuated to the Khanty-Mansiysk National Okrug.
10 thousand boxes of matches a year
During the first months of the war, the enemy deeply penetrated into our country and occupied the city where our main match enterprises were located: On June 28,1941, Minsk was captured, on June 29 – Liepājaand, Klaipeda, July 1 - Riga, July 4 - Pinsk, July 9 - Pskov, October 6 - Bryansk, October 13 - Kaluga, in the occupied territories there were 15 companies of match production, which accounted for more than 70% of production capacity of the match industry in the country.
Ugra residents for the Defense Fund
The hard-workers of Ugra made a significant contribution in order to provide the economic conditions needed for the victory of the Soviet people in the Great Patriotic War.
In total, during the war, the population of the Khanty-Mansiysk National Okrug donated about 58 million rubles, government bonds and jewelery to the Defense Fund. These funds were used for the production of military equipment.
In total, during the war, the population of the Khanty-Mansiysk National Okrug donated about 58 million rubles, government bonds and jewelery to the Defense Fund. These funds were used for the production of military equipment.
"Special volunteers"
Strategic human reserves were continuously formed in order to restore the Red Army's losses suffered during the winter counter-offensive under Moscow, in the deep rear. It was done also with the help of special settlers – fishermen.
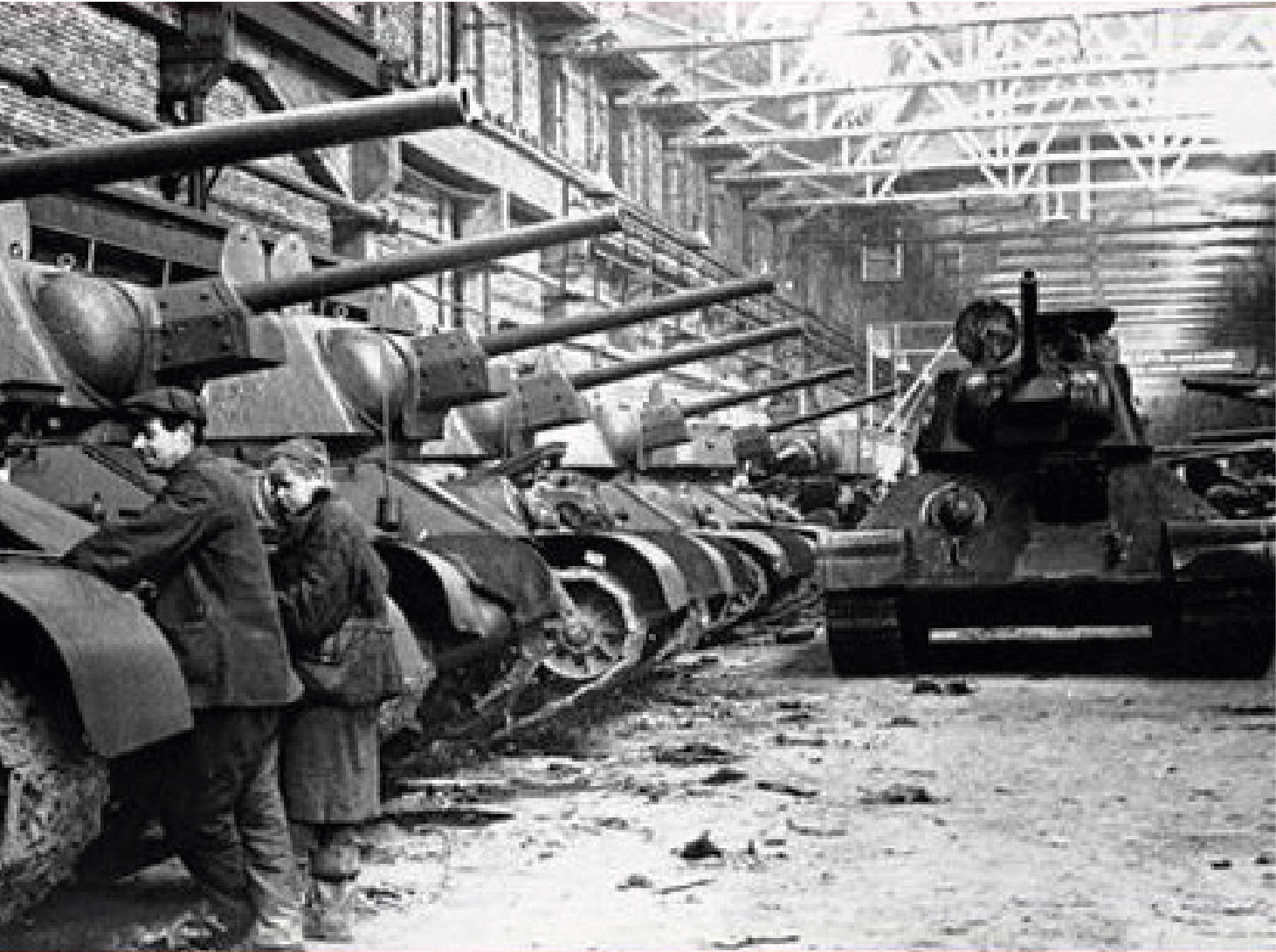
Named tanks
During the war, the inhabitants of the Laryaksky district of the Khanty-Mansiysk national district took part in the collection and transfer of funds for the construction of battle tanks for the Red Army.
From the information published in the newspaper "Stakhanovets" of the war period it is known that these funds were used to build tanks with the personal inscriptions: "Omsk sportsman", "Tambov collective farmer", "Omsk collective farmer", "Omsk Komsomolets", "Fighting friends", " Pioneer "tank" Baby "
From the information published in the newspaper "Stakhanovets" of the war period it is known that these funds were used to build tanks with the personal inscriptions: "Omsk sportsman", "Tambov collective farmer", "Omsk collective farmer", "Omsk Komsomolets", "Fighting friends", " Pioneer "tank" Baby "

Newspaper "Stakhanovets"
During the war years, district and regional newspapers were published in the Khanty-Mansiysk National Okrug: Stalin's Tribune, Kolkhoznik, For Bolshevik Collective Farms, Stalin's Way.
Front oil
The factories of the regional oil industry from 1942 until the end of the war worked steadily and made a profit. In 1943, they brought in a profit of 102.3 thousand rubles, for which they received the 3rd All-Union Prize. In total, 8 creameries operated on the territory of the district during the war years, which produced 3960.1 centners of oil for the needs of the front and rear.
Ukrainian Theater of the Far North
Even during the war years, film screenings and performances were held in Khanty-Mansiysk, they organized concerts - people tried to forget about the hardships of the war at least for a while. The newspaper publishes a poster for January 1942 of the Ukrainian Theater of the Far North. The unusual name was explained by the fact that many Soviet theaters, including those from Ukraine, were evacuated to the Urals and Siberia during the war.
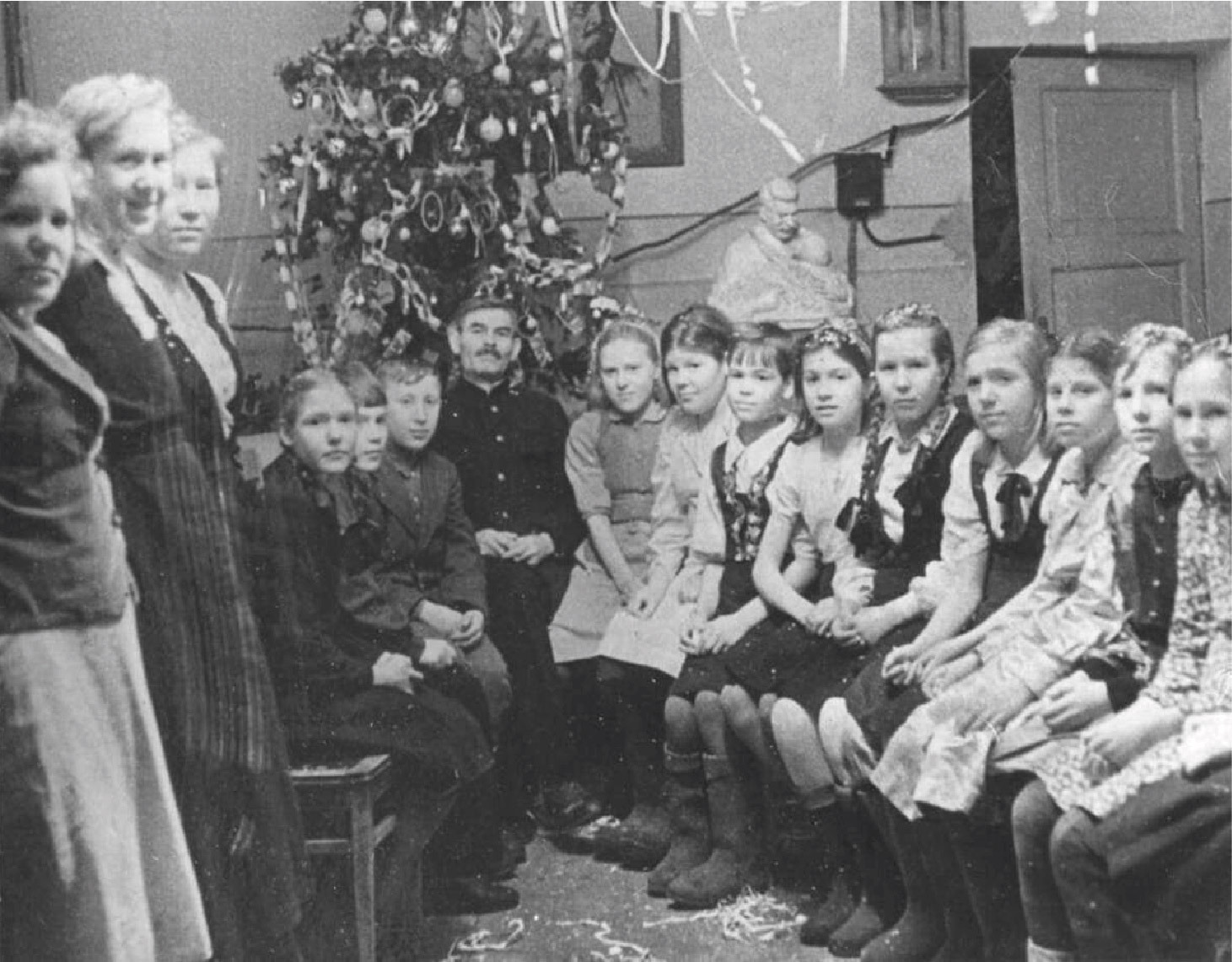
Wartime tree
The main symbol of the holiday - the New Year tree - was present in the trenches, in hospital wards, and in small schools in the most remote villages of the country. At the front, cartridges and empty cans were used as decorations, in the rear - boats and lanterns made of cotton and paper, less often - factory toys.
Fighting typhoid
In the winter of 1944-1945, the village of Nizhnevartovskoye suffered more misfortune - an epidemic of typhus broke out. Pavel Karpovich Sitnikov, who worked in 1944 as the director of the Nizhnevartovsk seven-year school, recalled that in the winter of 1944 an epidemic of typhus broke out in the village. Classes at the school were discontinued, an infirmary was deployed in the school building, and teachers were mobilized to fight the epidemic.
Letters from the front
The letters from the front are of historical importance. They were written on scraps of newspapers, granary books, between the lines. They wrote on a simple piece of paper and folded it into a triangle, since there were not enough envelopes. Letters were sent not only from the front, but also from the rear. Tenderness and love, support of loved ones, wives, mothers gave the soldiers additional strength, carried an awareness of the importance of peace over their heads, a joyful calm life for their families and children. That's what our grandfathers fought for! So that we now study, read books, make friends, live without war, without fascism and enslavement.
International Women's Day
The issue of "Stalin's Tribune" dated March 8, 1944 was dedicated to the labor deeds of Soviet women.
"The women of our district! Give all your strength and knowledge to the cause of the complete liberation of our Motherland from the German fascist invaders and the final defeat of the enemy, "the newspaper throws its slogan.
And the women of the district, young and old, give their last strength to the front without any calls.
"The women of our district! Give all your strength and knowledge to the cause of the complete liberation of our Motherland from the German fascist invaders and the final defeat of the enemy, "the newspaper throws its slogan.
And the women of the district, young and old, give their last strength to the front without any calls.
